Key Principles#
Once installed, the plugin can be used in several different ways within QGIS:
Through the toolbar buttons and items within the ‘Plugins’ menu. This is the simplest way to run the plugin.
Through the processing toolbox. This gives more options and allows for more automation. This includes chaining with other algorithms using the graphical modeller. (If you can’t see the processing toolbox activate it in the menu View -> Panels -> Processing Toolbox.)
This plugin has an API which can be used from the Python Console within QGIS. This allows access to all WNTR functionality.
To experiment quickly, you can load an example from the ‘plugins’ menu.
Whilst the plugin is very flexible in how it’s used, the key principles are the following four steps:
Model Creation. The model is a set of regular QGIS layers from any data source. Layers can either be created using the ‘Create Template Layers’ processing algorithm; or imported from EPANET files using the tools provided in the processing toolbox; or you can create them manually.
Node layers are junctions, reservoirs and tanks. They are represented by point geometry
Link layer are pipes, pumps and valves. They are represented by line geometry.
You only need to create and use the layers that you want.
Model Editing. The layers are normal QGIS layers and can be edited / modified / processed / styled / automated in the same ways as any other QGIS layer. In particular:
Digitize from any of the enormous range of data that QGIS can handle.
Snapping tools can be used when drawing the network to make sure that nodes and links connect. Note that this is optional, as the plugin will ‘snap’ the layers when running the model.
Pipe lengths can be calculated automatically.
Elevations can be added to nodes from other sources using either expressions or processing tools..
External data sources or any other layers can be used as background maps or data sources for drawing the network.
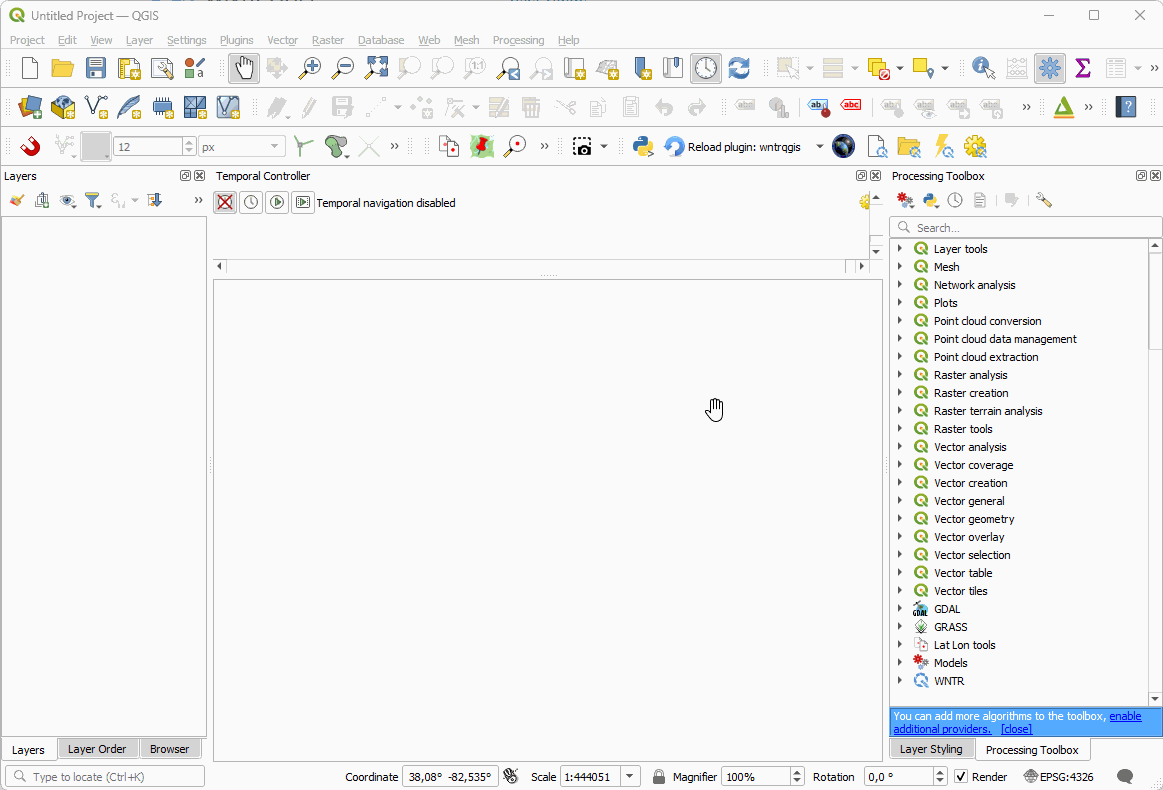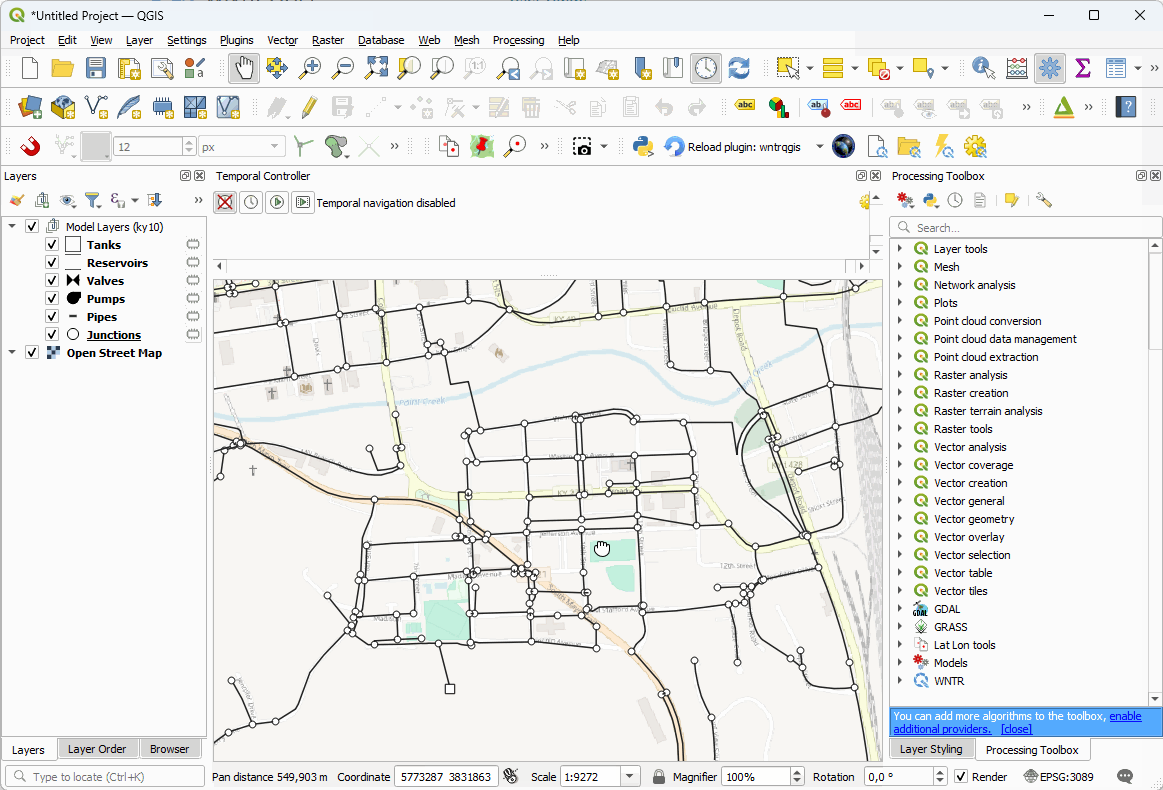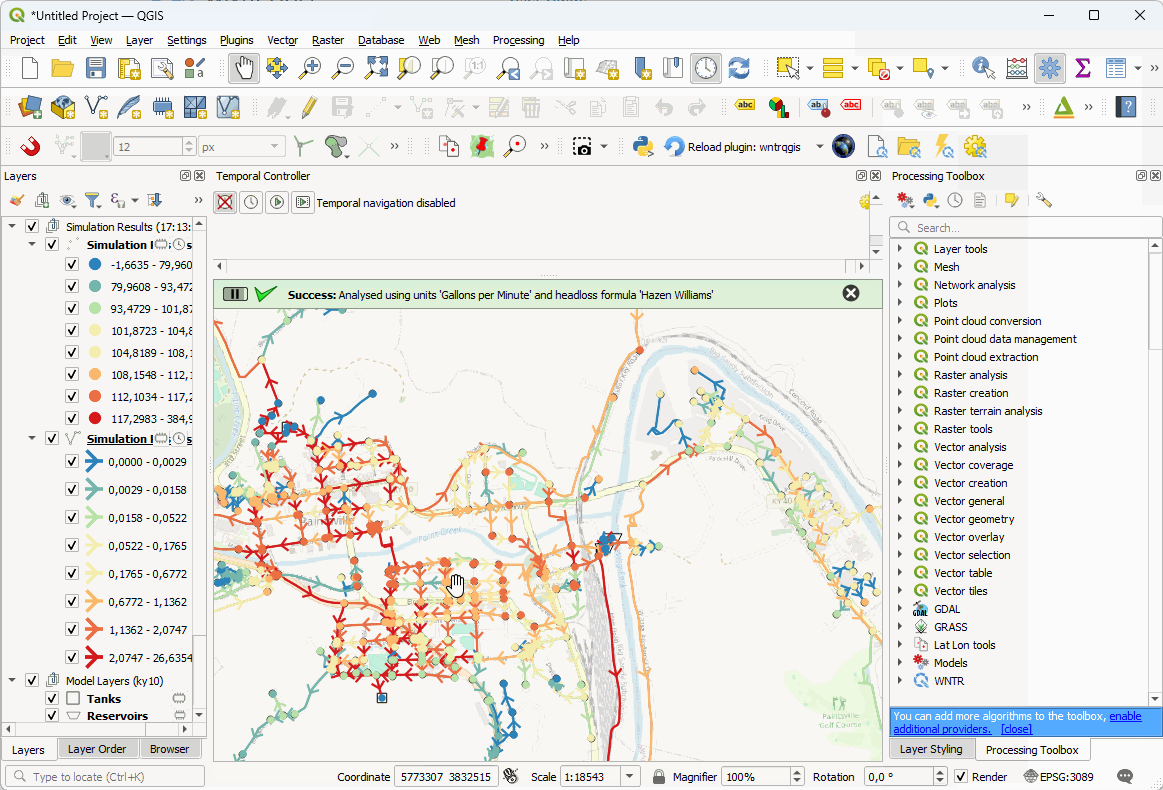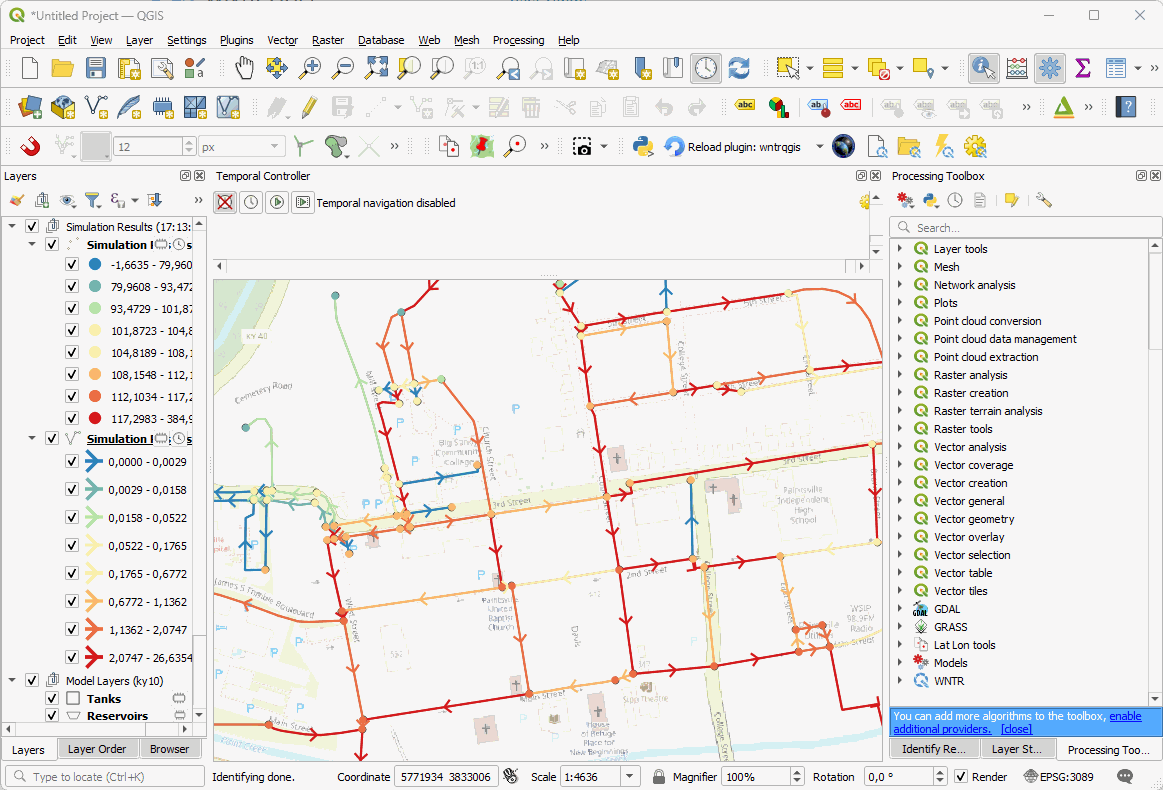
Running the simulation. The plugin will load your nodes, links, patterns, curves and options into WNTR and run the model. It will then process the output into a new link and node layer containing all calculated results. Configure your analysis options to exploit the full power or WNTR and EPANET.
Viewing the results. Use all the power of QGIS to view and analyse your results.
Use all of QGIS’s styling functions to look at all the results in nodes and links - pressure, flow, head, etc.
Use QGIS’s temporal manager to view how the results change over time.